Introduction
Cannabis belongs to the family of Cannabaceae; known to produce a unique family of terpeno-phenolic compounds called cannabinoids. The most well-known are Cannabidiol (CBD), the main component in industrial hemp, and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component in Marijuana. Legality of cannabis varies by country. The policy of use in most countries is regulated by the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961), the Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971) and the Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988). More than 0.3% THC is considered to be illegal and not accepted for use and sale in many parts of the world.
In the United States, California became the first state to legalize the medical use of cannabis with the passage of the Compassionate Use Act of 1996. In 2012 Colorado and Washington became the first states to legalize recreational use. As of November 2018, ten states (Alaska, California, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Nevada, Oregon, Vermont, and Washington), the District of Columbia, and the Northern Mariana Islands have legalized the with its commercial sale permitted in all except Vermont and D.C. Uruguay and Canada are the only sovereign states with fully legalized nationwide consumption and sale of recreational cannabis. Countries that have legalized the medical use of cannabis include Australia, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Cyprus, Finland, Germany, Greece, Israel, Italy, Norway, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Peru, Poland, and Thailand. In South Africa, it is legal to possess and cultivate, but not sell.
With legalization, many companies are riding on the CBD wave and developing potential applications in order to garner a share in the market. The different combinations of CBD and THC that are possible creates huge opportunities for these players particularly in food, cosmetic and medical product areas. In the food and beverages area, cannabis infused food in the form of edibles and drinkables have already hit the market. Production of cannabis edibles requires appropriate testing for bio contaminants and pathogens. Infused edible products must indicate on the label that they have been tested for pesticides, heavy metals, mold, and residual solvents. No public safety guidelines or U.S. Food and Drug Administration label requirements exist, yet people with chronic medical conditions – cancer, Parkinson’s disease, ALS, Multiple sclerosis use these products for pain and symptom management.
Food/Beverages
Hemp oil products containing the non-psychoactive cannabinoid CBD or cannabidiol are available as capsules, chewable gummies, tinctures, and infusededibles (brownies, cookies, lollipops, chocolate candy).











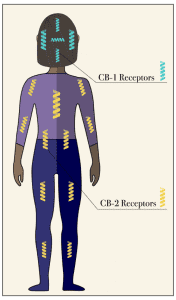

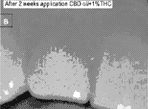
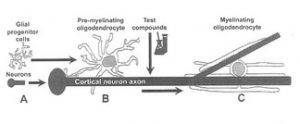
 nanotechnology transdermal path for delivering THC and CBD through skin penetration reaching the blood stream without altering the skin structure. Following the legalization, there have been many studies commissioned to understand the mechanistic pathways.
nanotechnology transdermal path for delivering THC and CBD through skin penetration reaching the blood stream without altering the skin structure. Following the legalization, there have been many studies commissioned to understand the mechanistic pathways.